A Comprehensive Look into Trauma Disorders and Their Treatments
Written By
GET IN TOUCH WITH US
Follow Us On Social Media
Receive A Call
A Comprehensive Look into Trauma Disorders and Their Treatments
Understanding the nature of trauma disorders and discussing valuable insights to help you cope with the impact of trauma and move toward healing and recovery.
— by Kyle Lakey
What Are Trauma Disorders?
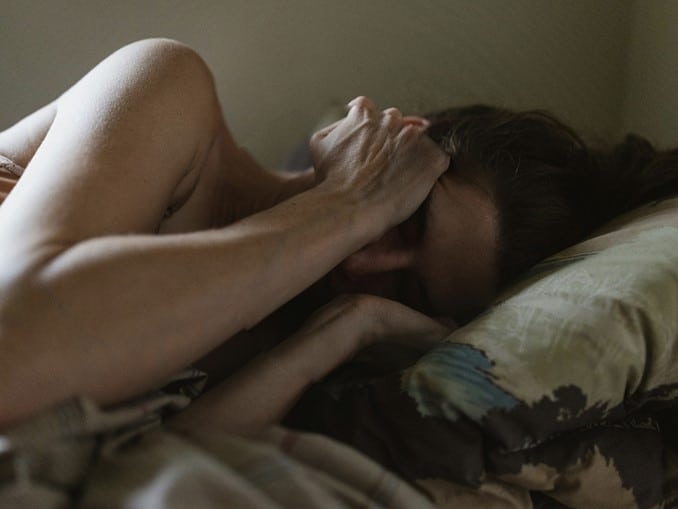
Trauma disorders refer to a set of mental health conditions that arise from experiences of trauma. These experiences can be physical, emotional, or psychological, such as accidents, abuse, violence, and natural disasters. These disorders occur when an individual’s ability to handle a traumatic event is overwhelmed, leading to persistent symptoms that can cause distress and impairment in daily life.
Trauma disorders can occur abruptly or persistently and can manifest in different ways. They can impact individuals of any age and result in an array of indications, such as nervousness, despair, recollections, and bad dreams. Traumatic occurrences can have enduring impacts on one’s psychological well-being and could even alter their perception of their surroundings.
Types of Trauma Disorders
PTSD is perhaps the most well-known trauma disorder which alone affects millions every year. But many other conditions are often seen in the aftermath of traumatic experiences. There are several types of trauma disorders, each with its own unique set of symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment approaches.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
PTSD is a mental health disorder that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, combat, sexual or physical assault, or a serious accident. PTSD is characterized by a range of symptoms, including flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety or agitation, and avoidance of triggers associated with the traumatic event. These symptoms can be severe and long-lasting and can significantly impact a person’s ability to function in daily life. PTSD can be treated with therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Acute Stress Disorder
Acute stress disorder is a mental health disorder that is similar to PTSD but occurs directly after a traumatic event. Acute stress disorder shares similarities with PTSD, but it has a shorter duration. While PTSD symptoms may take several months to appear and persist for years, ASD symptoms appear right away and usually last only a few months.
Adjustment Disorder
Adjustment disorder is a mental health disorder that can develop after experiencing a stressful life event, such as a divorce, job loss, or financial hardship. Symptoms may include depression, anxiety, and behavioral problems. Adjustment disorder is often a temporary condition that can be treated with therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Reactive Attachment Disorder
Reactive attachment disorder is a mental health disorder that can develop in children who have experienced significant trauma, such as neglect or abuse. Symptoms may include a lack of emotional attachment to caregivers, emotional detachment, and difficulty forming relationships. Children with reactive attachment disorder may also display behavioral problems such as aggression or self-harm. Treatment for reactive attachment disorder often involves therapy aimed at helping the child develop healthy attachment relationships.
Disinhibited Social Engagement Disorder
Disinhibited social engagement disorder is a mental health disorder that can develop in children who have experienced significant trauma. Symptoms may include indiscriminate, overly friendly behavior toward strangers, a lack of boundaries, and difficulty understanding social norms. Children with disinhibited social engagement disorder may also have difficulty forming healthy attachment relationships.
Complex Trauma (C-PTSD)
Complex trauma is a form of trauma that results from enduring or recurring exposure to traumatic events or experiences. These events can include childhood abuse or neglect, domestic violence, or combat. Complex trauma can greatly affect a person’s mental health and overall well-being and cause a lifetime of issues if left untreated. It can cause various symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and challenges in forming healthy relationships.
Relational Trauma
Relational trauma is a type of trauma that occurs within the context of intimate relationships, such as emotional or physical abuse from a partner or family member. Usually, the person causing harm or abuse is someone that the victim has known and trusted in the past. As a result, recovering from relational trauma can be extremely difficult, leading to feelings of self-doubt, confusion, and shame. The effects of this type of trauma can be extensive, impacting a person’s capacity to trust others, form healthy relationships, and feel secure in their own body.
Causes of Trauma Disorders
Trauma disorders can be caused by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. The severity of the event, as well as the individual’s perception of the event, can impact the development of a trauma disorder as well as the severity and type. Traumatic events can include natural disasters, accidents, violence, sexual abuse, or other life-threatening situations. Trauma can also result from ongoing experiences of abuse, neglect, or other forms of adversity.
Symptoms of Trauma Disorders
Symptoms of trauma disorders can vary widely depending on the type of disorder and the individual’s unique experience of trauma. Common symptoms of trauma disorders can include:
- Intrusive thoughts or memories of the traumatic event: Recurring thoughts or memories of the traumatic event that can be difficult to control or stop.
- Nightmares or flashbacks: Re-experiencing the traumatic event through vivid and distressing dreams or sensations.
- Avoidance of reminders of the traumatic event: Avoiding people, places, or things that remind the individual of the traumatic event.
- Hypervigilance or heightened arousal: A state of increased alertness and sensitivity to potential threats or danger, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, or trembling.
- Negative changes in mood or cognition: Negative changes in thoughts or emotions, such as feelings of guilt, shame, or hopelessness.
- Dissociation or feeling disconnected from reality: A feeling of detachment or disconnection from oneself or the world around them.
Symptoms of trauma disorders can cause significant distress and impairment in daily life, including difficulties with relationships, work, and other areas of functioning.
Treatments for Trauma Disorders
Trauma disorders are treatable, and several evidence-based treatments are available. The most effective treatments for trauma disorders tend to be those that are tailored to the individual’s unique needs and experiences and typically include a combination of medication and therapy. Medication is a reliable way to manage symptoms of trauma disorders, while therapy can bhelp people gain insight into their thoughts and behaviors and develop effective coping strategies to manage difficult emotions and situations.
Some commonly used treatments for trauma disorders include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy that helps individuals identify and change negative patterns of thought and behavior that are affecting their mental health. The goal of CBT is to help individuals develop coping strategies to manage difficult situations and improve their overall quality of life. CBT is commonly used to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is a therapy that uses guided eye movements to help individuals process traumatic memories and reduce negative emotions associated with them. EMDR is based on the idea that traumatic memories are stored differently in the brain than non-traumatic memories, and that eye movements can help the brain process traumatic memories in a more adaptive way. EMDR is commonly used to treat PTSD and other trauma-related disorders.
Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE)
Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE) is a therapy that involves gradually exposing individuals to the source of their trauma in a safe and controlled environment, with the goal of reducing their fear and anxiety over time. PE is based on the idea that avoidance of traumatic memories and situations can actually increase anxiety and other symptoms of trauma. By gradually exposing individuals to the source of their trauma, they can learn to develop coping strategies to manage their symptoms and reduce their fear and anxiety.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is a type of talk therapy that focuses on teaching individuals skills to manage their emotions and improve their relationships with others. DBT is based on the idea that individuals who struggle with mental health conditions often have difficulty regulating their emotions and communicating effectively with others. DBT teaches individuals skills such as mindfulness, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness to help them manage their symptoms and improve their relationships.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic Therapy is a type of talk therapy that aims to help individuals develop insight into their unconscious thoughts and emotions and how they affect their behavior. The goal of psychodynamic therapy is to help individuals gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their relationships and to develop effective coping strategies to manage difficult emotions and situations. One of the key principles of psychodynamic therapy is the idea that past experiences and relationships can impact current thoughts and behaviors. A therapist may use techniques such as free association, dream analysis, and interpretation to help the individual explore their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in a safe and non-judgmental environment.
Medication
Certain medications, such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of trauma disorders. It’s important to note that medication alone is usually not enough to fully treat trauma disorders and is typically used in conjunction with therapy. Medication can be helpful in managing symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances and can make it easier for individuals to engage in therapy and other forms of treatment.
Get Help for Trauma Disorders at Psyclarity Health
At Psyclarity Health, we offer evidence-based treatments for trauma disorders. Our team of mental health professionals is dedicated to helping individuals overcome trauma and live fulfilling lives. We understand that each person’s experience of trauma is unique, and we work closely with each individual to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their needs. Contact us today to learn more about our services.









