Coping Strategies and Treatment Methods for PTSD
Written By
GET IN TOUCH WITH US
Follow Us On Social Media
Receive A Call
Coping Strategies and Treatment Methods for PTSD
Managing PTSD can be a long and challenging process, but there are several coping strategies and treatment methods that can help individuals to manage their symptoms effectively.
— by Carl Yazbek
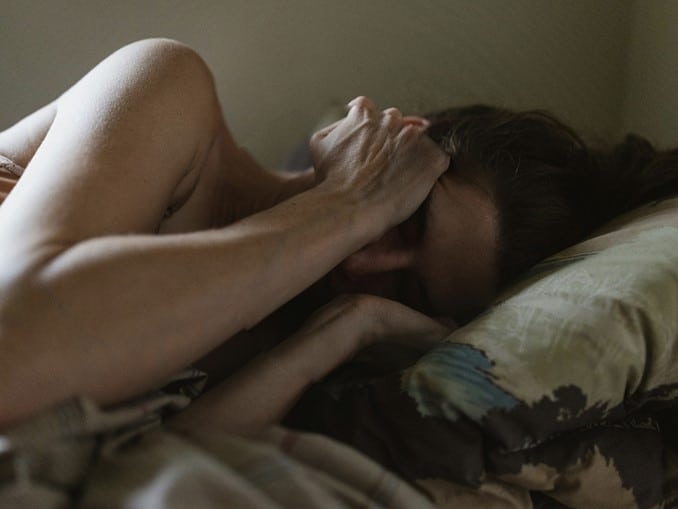
PTSD is a mental illness that develops after experiencing overwhelming terror. It can result from trauma such as natural disasters, military combat, rape, accidents, or losing a loved one. People who have PTSD may experience flashbacks, nightmares, intense anxiety, depression, and other symptoms that can severely impact their quality of life. Women tend to experience it more than men, possibly due to domestic violence and sexual abuse. PTSD can also affect rescue workers and the families of the victims. About 5.2 million people in America experience PTSD annually. However, not everyone who experiences trauma will develop the condition.
Co-Occurring Disorders
Trauma can result in various physical and psychological health issues, including PTSD, which can cause anger, anxiety, depression, emotional numbness, and other problems. Common issues that may occur alongside trauma include sleep disturbances, alcohol addiction, broken relationships, and flashbacks. Trauma survivors may also struggle with eating disorders, self-destructive behavior, or suicide. At Psyclarity Health, our mental health treatment programs provide complete care, including dual diagnosis treatment for all co-occurring mental disorders.
Causes of PTSD
PTSD is a disorder caused by exposure to traumatic events. Inherited mental health issues, temperament, and chemical imbalances in the brain can intensify symptoms.
The following events can cause PTSD:
- Threats with a dangerous weapon or death
- War or armed combat
- Near-death experiences, kidnapping, or being taken hostage
- Assault, including sexual assault, torture, robbery, and mugging
- Diagnosis of a fatal illness
- Death of a loved one
- Childhood abuse
- Domestic abuse
- Physical neglect
- Surviving disasters
Risk Factors for PTSD
Individuals who have experienced traumatic or frightening events are more likely to develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Factors that increase the risk of developing PTSD include:
- Previous exposure to trauma, such as childhood abuse
- Repeated exposure to life-threatening situations
- Mental illness, such as depression or anxiety
- Lack of support to cope with distressing experiences
- Family history of mental health issues
- Substance abuse or alcohol addiction
- Hazardous job roles
- Biological predisposition to stress responses due to brain chemistry
Signs and Symptoms of PTSD
After a traumatic event, people may experience typical responses such as thinking about the event, sleeplessness, lack of focus, sadness, or discomfort. However, some people may have severe reactions. PTSD symptoms typically emerge within a month but may be delayed. These symptoms can impact work, relationships, and social life.
Signs of PTSD in someone you know may include:
- Excessive worry and anxiety
- Depression
- Denial or irrational guilt
- Agitation or anger
- Nightmares and terrors
- Insomnia
- Avoidance and isolation
- Difficulty remembering details of the trauma
- Exaggerated response to startle
- Numbness or disconnection
- Loss of interest in usual activities
- Persistent negative thoughts or feelings
Coping Strategies for PTSD
Coping strategies are techniques or activities that individuals can use to manage their symptoms and reduce stress. Here are some of the most effective coping strategies for PTSD:
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation can help to reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm. These techniques can be practiced anywhere, and they can be particularly helpful during times of stress.
Physical Activity
Physical activity, such as running, swimming, or yoga, can help to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Exercise has been shown to have a positive effect on mood, and it can help to increase feelings of well-being.
Social Support
Maintaining social connections with friends and family members can be an effective way to reduce symptoms of PTSD. Support from others can help individuals to feel less isolated and can provide a sense of community and belonging.
Treatment Methods for PTSD
In addition to coping strategies, there are several treatment methods that can be used to manage symptoms of PTSD. Treating post-traumatic stress disorder requires a comprehensive approach with the help of a mental health professional, which may involve medicines, psychotherapy, and behavioral therapies. Even after treatment, some symptoms may persist. However, effective treatment can minimize physical and emotional side effects, allowing patients to return to regular daily activities. Here are some of the most effective treatment methods for PTSD:
Medication
Treatment programs may include medications such as blood pressure medication to reduce nightmares and traumatic memories. Medication can be used to manage symptoms of PTSD, particularly in conjunction with therapy. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications are often prescribed by mental health professionals to help manage symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia.
SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are the most commonly known antidepressants. SSRIs can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. They may also be helpful in improving cognitive function affected by these symptoms. Common SSRIs include sertraline, fluoxetine, and paroxetine.
SNRIs
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) can be effective in treating both major depressive disorders and PTSD. They function similarly to SSRIs but also inhibit the reuptake of norepinephrine. Venlafaxine is a commonly used SNRI for treating PTSD.
Anxiolytics
Anxiolytics are medications that help treat anxiety disorders, like GAD, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder, by reducing anxiety, fear, and tension. Benzodiazepines reduce anxiety by enhancing GABA neurotransmitters in the brain, while other anxiolytics, such as buspirone, affect the levels of serotonin and dopamine in the brain.
Anti-Psychotic Medication
Antipsychotics may be used to treat extreme cases of PTSD by alleviating psychosis symptoms and improving mood. These medications alter brain chemicals to alleviate symptoms like delusions and hallucinations in conditions like schizophrenia and severe depression.
PTSD Therapy
Therapy can be an effective way to manage symptoms of PTSD. Different types of therapy can be used to treat PTSD, including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR). Therapy can help individuals to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs and to develop coping strategies for managing symptoms and handling triggers in the long term.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a form of therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It can help individuals with PTSD to identify and challenge negative thoughts and beliefs and to develop coping strategies for managing symptoms.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR)
EMDR is a form of therapy that involves recalling traumatic events while engaging in rapid eye movements. This process can help to reduce the intensity of negative emotions associated with traumatic memories.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to the traumatic event in a controlled and safe environment. This process can help individuals to confront their fears and to develop coping strategies for managing symptoms.
Family Therapy
Family therapy is a helpful treatment for PTSD. It involves all or some family members to improve communication and relationships. A therapist helps identify and change patterns of behavior contributing to the person’s symptoms. It helps the family to support and cope with the disorder.
Group Therapy
Group therapy for PTSD can provide support and education about treatments. Interacting with others who share similar experiences can create a sense of camaraderie and help individuals express their feelings.
Self-Care for PTSD
Self-care is an important aspect of managing PTSD. Here are some self-care strategies that can be helpful for managing symptoms of PTSD:
Get Enough Sleep
Getting enough sleep is important for overall well-being. It’s important to establish a regular sleep routine and to avoid caffeine, alcohol, and other substances that can interfere with sleep.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a healthy, balanced diet can help to promote physical and emotional well-being. It’s important to focus on nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins and to avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
Engage in Relaxing Activities
Engaging in relaxing activities such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or practicing mindfulness can help to reduce stress and promote a sense of calm.
Avoid Drugs and Alcohol
Drugs and alcohol can worsen symptoms of PTSD. It’s important to avoid using these substances and to seek professional help if needed.
Residential PTSD Treatment
Psyclarity Health offers residential trauma treatment programs lasting a few weeks to monitor the patient’s condition. Take our free online assessment to start the admissions process and receive immediate help. If you or someone you know is struggling with PTSD, it’s important to seek professional help and support. Remember that recovery is a process, and everyone’s journey is unique. With time and effort, it’s possible to heal from the effects of trauma and move forward toward a brighter future.
Benefits of Trauma Therapy at a Treatment Center
Understanding your trauma, its causes, and your reactions is crucial. Identifying your therapy goal, whether it’s to share your story, raise awareness, find peace, or confront your abuser, can help you determine which issue to address in therapy. CBT, talk therapy, and other trauma therapies can help with phobias, safety concerns, shame, advice, and environmental influences.
Trauma therapy can help individuals identify and understand the cause of their trauma and find constructive ways to cope with symptoms. Psyclarity Health’s trauma counselors can help you develop a treatment plan that addresses immediate concerns while promoting long-term wellness. Learning preventative methods such as self-harm protection, trauma processing, anxiety management, and healthy coping skills can help you stay on track with your recovery.
Get Help for PTSD and Trauma
PTSD can cause other issues like depression, anxiety, substance abuse, eating disorders, and suicidal behavior. These issues can affect relationships, work, health, and daily life. PTSD can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right coping strategies and treatment methods, it’s possible to manage symptoms effectively. At Psyclarity Health, our experienced counselors provide effective PTSD treatment programs to help patients live fulfilling life. We specialize in inpatient trauma therapy and treat co-occurring disorders. Contact us today for help with post-traumatic stress disorder or counseling after a traumatic event.









